Like the ‘Internet of Things’ and ‘Artificial Intelligence’, ‘edge computing’ has escaped the buzzword bubble and is now a tangible technology that is gaining significant traction. And with businesses across the globe keen on implementing the latest IT practices to stay ahead of the competition, this paradigm is only set to become more popular.
But what does edge computing really mean? How can the concept help organisations build relevant IT products and services? Let’s explore…
The drawback of centralised systems
In the early days of computers, there were centralised systems that performed the majority of work on-site. Today, we have access to personal computers, allowing us to take our self-contained device of computing power anywhere we go.
However, even though we use our own computers, we still access a plethora of centralised cloud-based services like Office 365, G-suite, and Dropbox on a daily basis. Additionally, AI-powered devices like Google Chromecast and Amazon Echo have also become an integral part of our lives.
And because these centralised data repositories are truly phenomenal, there are millions of businesses worldwide that rely on their infrastructure and computing power. But there’s a catch. Currently, there are only four global cloud providers — Amazon (with over 32% of the market share), Microsoft, Google, and IBM.
This means that all data is created and processed at centralised storage hubs by only a handful of providers, and there isn’t much growth left in the cloud space. Anything that can be centralised has already been centralised, and new opportunities now lie at the ‘edge’.
Defining edge computing
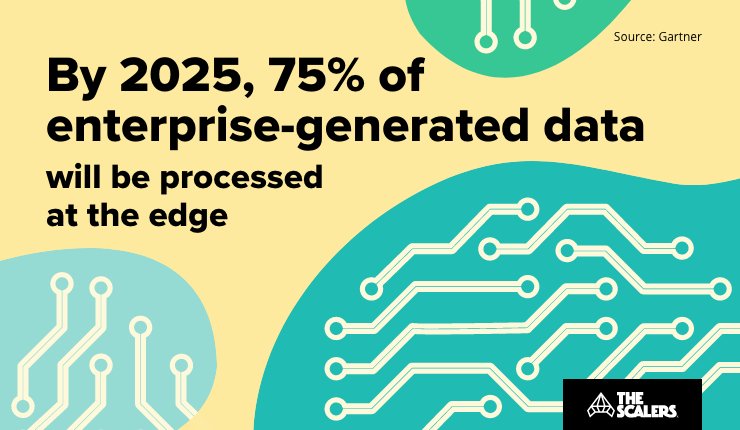
Wikipedia defines edge computing as ‘a distributed computing paradigm that brings computation and data storage closer to the location where it’s needed — to improve response time and save bandwidth’. In layman’s language, it simply means processing data closer to the source.
Let’s consider a simple scenario. Oil and gas failures can prove to be disastrous if not handled immediately. This means that their assets need to be monitored 24/7 and in real-time. One solution is to set up a centralised cloud monitoring system. But, because oil and gas plants are usually located in remote locations, quality connectivity to the cloud is not guaranteed. And, the response time of a centralised system might be delayed too.
However, by enabling real-time analytics and processing data closer to the asset, there is a lesser dependency on the cloud. This ensures a quick response time and low latency. And that is what edge computing can do for you.
The cloud remains the cloud — it simply comes closer to where you are.

The benefits of edge computing
Some people refer to edge computing as the ‘cloud killer’. However, in reality, it is simply an evolution of the cloud. Businesses will continue to use the cloud to create, process, and store operational data. But by using edge computing, they can also efficiently process data for time-sensitive applications.
Some of the notable benefits of edge computing include:
Lower latency:
In an era where speed is everything, edge computing helps locate key processing tasks closer to end-users, in turn, delivering faster and more responsive services.
Better security:
Because information does not have to be transmitted to the cloud, users do not have to worry about confidential or sensitive data being stored anywhere.
Lower bandwidth:
When 100 devices transmit the same data to the cloud, you’re bound to have a bandwidth problem. However, because edge computing processes data from a single source, it will not tax your bandwidth.
Applications of edge computing in 2021
1. Real-time medical diagnosis
Medical IoT devices that are at the edge can detect abnormal health conditions faster and with greater ease. This will lead to quicker response times and more timely medical diagnosis and treatments. If implemented the right way, edge computing can steer the world away from reactive treatments and towards real-time, AI-based predictive healthcare.
Further, monitoring devices such as glucose monitors that aren’t required to be connected to the cloud can simply be connected to an edge system instead. This system will be present at the hospital site and can process and maintain data locally. Doing this not only ensures data privacy but also allows healthcare workers to monitor patients’ behaviors in real-time.
2. Energy consumption
Edge computing is one of the core technologies implemented in smart grids that allow enterprises to manage their energy consumption. Through IoT devices and sensors that are connected to an edge platform, large factories and establishments can monitor and analyse their energy use and optimise it to conserve energy.
3. Cloud gaming
Cloud gaming has gained significant popularity in the last decade. However, because it streams a live feed of the game directly to the device itself, it is highly dependent on latency. And so, by building edge servers closer to gamers, gaming corporations can provide users with a fully responsive, uninterrupted, and immersive gaming experience.
4. Smart homes
Smart homes rely heavily on IoT devices that collect and process data from around the house. Often this data is sent to a centralised remote server for storage. However, this existing architecture is expensive and not secure.
Instead, using edge computing and storing data closer to the smart home ensures that the backhaul time is reduced and sensitive information is protected. For instance, the time taken for smart devices such as Amazon’s Alexa to respond would be much faster.
What edge computing means for businesses: a conclusion
- Edge computing is transforming how data is being created, processed, and stored from millions of devices worldwide.
- The explosive growth of internet-connected devices, technology, 5G networks, and new applications that require real-time computing power continues to drive edge-computing systems.
- Autonomous vehicles, predictive maintenance, smart systems, and content delivery are a few of the many applications that will be transformed by edge computing in the years to come.
If you’re interested in exploring the possibility of building a fully integrated offshore team, feel free to reach out to us by filling out the contact form. One of our senior executives will get in touch with you within 24 hours.
Build Your Team,
Not Just a Contract
With The Scalers’ offshore dedicated development team, you get engineers who join your workflow for the long run. Grow steadily, stay flexible, and work with people who care about the product as much as you do.







